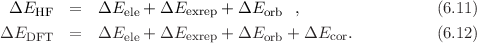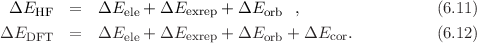6.6 Energy Decomposition Analysis (EDA)
The interaction energy between molecules can be calculated with the supermolecular
approach: one performs calculations for the supersystem and for the subsystems with
size-consistent methods and derive the interaction energy ΔE by taking the energy
difference. The energy decomposition analysis (EDA) allow a partitioning of the
Hartree-Fock (HF) or DFT interaction energy in physically meaningful contributions: the
classical electrostatic interaction ΔEele, the exchange-repulsion ΔEexrep, the orbital
relaxation energy ΔEorb and additionally for DFT the correlation interaction ΔEcor:
Further details and derivations of the different energy contributions can be found
in [106].
6.6.1 How to perform
The EDA scheme is implemented in the module ridft and can be done with
RI-Hartree-Fock and with all local, gradient corrected, hybrid and meta density
functionals (please note that the functionals included in the XCFun library are not
supported!).
- Calculation of the subsystems:
In HF and hybrid DFT calculations please insert $scfdenapproxl 0 in the
control file, at least in a second run. The EDA scheme needs the exchange and
Coulomb energies of every system separately. After the subsystem calculation
you will find under $subenergy the different energy contribution to the total
energy of the system: the one electron energy, Coulomb- and exchange energy,
correlation energy in case of DFT calculations, nuclear repulsion energy and
optionally the dispersion energy.
- Preparation of the supersystem control file:
First run define for the supersystem and take for consistency the same basis set
and the same method (i.e. the same functional and the same grid). Please
use in case of DFT calculations not the multiple grids m3 to m5, because
this would lead to erroneous orbital relaxation energies. If the subsystems
are open-shell species the occupation in the EHT submenue of define of
the supersystem must be chosen open-shell, too. For open-shell systems
the Fermi-smearing is recommended. The sequence of the supersystem
coordinates must have the same sequence as the subsystem coordinates. In
the case of HF and hybrid DFT calculation use again $scfdenapproxl 0.
Then please insert in the control file :
$subsystems
molecule#1 file=sub1/control
molecule#2 file=sub2/control
If you use the supermolecular basis set for the calculation of the monomers please
insert after $subsystems the option copo:
$subsystems copo
molecule#1 file=sub1/control
molecule#2 file=sub2/control
It is possible to generate orthogonal product wave functions when you use opro
instead of copo. But with this choice it is not possible to calculate the different
energy contributions of the interaction energy.
You can choose at most ten subsystems.
- Generation of the product molecular wave functions:
The module promowa generates RHF and UHF product molecular wave functions.
The new (product) start vectors can be found in the files mos for closed-shell
systems or in alpha and beta for open-shell systems. Please note that the
molecular orbitals of the different subsystems are not orthogonal to each
other.
- Energy decomposition analysis:
After the supersystem ridft calculation you will find the following output with the
different contributions of the interaction energy in Hartree:
----------------------------------------------------
| * Total Interaction energy = -0.0058700698 |
----------------------------------------------------
: * Electrostatic Interaction = -0.0134898233 :
: Nuc---Nuc = 18.2843363825 :
: 1-electron = -36.5372802833 :
: 2-electron = 18.2394540775 :
: * Exchange-Repulsion = 0.0112325934 :
: Exchange Int. = -0.0139477002 :
: Repulsion = 0.0251802936 :
: * Orbital Relaxation = -0.0036128399 :
.....................................................